Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a centralized file server connected to a network that lets multiple users in different locations access the same storage over the network or the internet. NAS devices are primarily used for data storage and file sharing requests, but over time they’ve evolved to embody a wide variety of solutions that can be used for more. They provide ideal storage solutions for file storage applications including streaming, storing frequently accessed video and image files, archives for backup and recovery, and hosting virtual desktop infrastructure. This article offers a detailed overview of network attached storage and how it works, its benefits and drawbacks, and an explanation of the different types of NAS available today.
Jump to:
How Does NAS Work?
Types of NAS Systems
Benefits of Using NAS
Limitations and Drawbacks of Network Attached Storage
NAS Use Cases
Bottom Line: Why Choose NAS?
What is Network Attached Storage?
Network attached storage is one of three main storage architectures used in enterprise environments, along with direct attached storage (DAS) and storage area networks (SAN).
NAS systems are connected to networks to facilitate efficient data storage, sharing, and retrieval. They provide a centralized location for the storage and management of digital content, making it accessible for authorized users and devices present on the local area network (LAN) or over an internet connection.
NAS software is run on its own operating system embedded in the device hardware, letting users configure and control the network and access data. The devices connect to networks by ethernet or WiFi. Some also have USB ports to connect other devices to them.
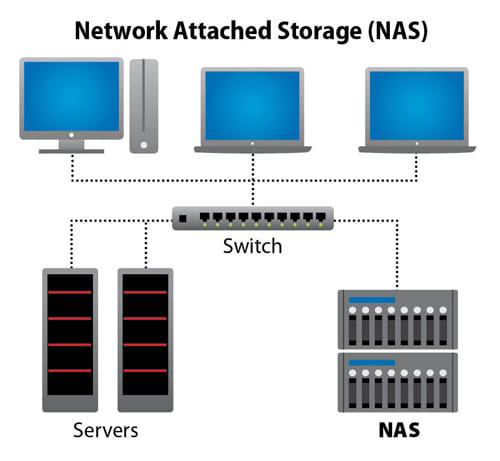
How Does NAS Work?
At the center of a NAS architecture are devices that hold a number of storage drives—typically between two and five. NAS devices can use either solid-state drives (SSDs) or mechanical hard disk drives (HDDs); while SSDs are faster, HDDs boast larger storage capacities at a lower cost. More drives can provide more capacity as well as failsafe redundancy.
Many NAS systems also use RAID, a Redundant Array of Independent Disks configuration that groups multiple storage disks together to allow for easy data replication and distribution. That way, if a disk fails, others can continue serving the system with little to no data loss.
NAS devices also hold integrated random access memory (RAM) and central processing units (CPUs) that serve as their brains, handling a multitude of tasks and operations from managing incoming data requests to executing various data transfer operations.
Types of NAS Systems
NAS solutions are categorized based on the size and outreach of the network into three types: home, small business, and enterprise.
- Home NAS. Designed for small-scale use in the home or private office, home NAS devices have user-friendly interfaces and offer features like automated backups and media streaming capabilities.
- Small Business NAS. NAS for small and medium-sized businesses caters to more substantial storage needs and advanced functionality suitable for a corporate setting. They often include built-in functionality for data security and protection while also supporting RAID configurations to safeguard critical information.
- Enterprise NAS. Enterprise-grade NAS systems are engineered to accommodate the colossal data storage and management requirements of large corporations and offer exceptional performance, expansive scaling capacities, and robust data protection mechanisms. Tailored for high-demand environments, they also include the speed and reliability necessary for managing extensive data repositories in complex organizational settings.
Benefits of Using NAS
The benefits and advantages of NAS systems extend far and beyond their primary purpose of making data readily available. They address a wide variety of technical needs, making them indispensable tools for data-reliant organizations.
Streamlined Data Management
Data organization and management are two of the biggest advantages of using NAS solutions, because they serve as unifying hubs for all digital assets and greatly simplify the organization, accessibility, and safeguarding of data. This aspect is particularly important for enterprises that regularly generate and handle substantial volumes of data and extensive digital media collections.
Cost-Effective Storage
NAS systems stand out as some of the most cost-effective long-term data storage solutions for large-scale applications. By eliminating the necessity for high-cost servers or top-tier hardware, NAS allows for a centralized storage environment at a more affordable cost. Its scalability also allows for the gradual expansion of storage capacity in tandem with evolving demands.
Enhanced Collaboration
NAS has the capability to enable multiple users to concurrently access and collaborate on files, making it well-suited for businesses centered around cooperative endeavors. NAS also fosters smoother file sharing, accelerates decision-making, and promotes collective efficiency.
Augmented Storage Capacity
Compared to other storage solutions, NAS devices offer a substantial boost in storage capacity at a fraction of the cost, alleviating data overload and bottlenecks.
Private Cloud Storage
NAS systems allow for the provisioning of private cloud storage capabilities, giving increased control and accessibility compared to public cloud storage and enabling businesses to maintain the privacy and integrity of confidential documents, personal files, and critical data.
Built-in Data Safeguards
Nearly all commercial NAS systems include automated software for the backup and recovery processes. This proactive approach ensures data integrity and greatly minimizes the risk of data compromises and loss due to unplanned events and catastrophes.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Network Attached Storage
Despite their numerous advantages and benefits, NAS systems have some limitations and drawbacks worth considering before investing in the technology at a large scale.
Limited Performance
While NAS systems can offer high performance, they aren’t as fast as SANs or DAS. While this is less of an issue for home and small business users, it could be limiting for enterprises running applications that need access to real-time data in large numbers.
Complexity
While NAS solutions are simpler than many alternatives, larger-scale enterprise NAS needs specialized expertise to set up and maintain. Poorly implemented systems can result in bottlenecks or decreased performance.
Initial Cost
While NAS systems tend to be cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment can be high for enterprise-level NAS—especially compared to direct attached storage solutions.
NAS Use Cases
Because NAS provides scalable, high-performance file storage systems to support intensive processing from a variety of applications, it can be used to improve productivity through a wide range of applications, including surveillance integration, support for virtualization, file sharing, and enhanced collaboration. Here are some of the most common use cases for NAS:
- Backup and recovery. From centralized storage to automated backups, NAS devices are used to minimize downtime and safeguard critical data during emergencies and cyberattacks. Network attached storage and data snapshots can complement an organization’s data strategy by offering immediate recovery of important files after an attack, saving time and money.
- High volume data. Enterprises streaming huge amounts of data to the cloud—for example, millions of image files—would suffer from cloud latency, but highly scaled enterprise NAS can store images and use cloud caching to maintain pointers to the on-premise files.
- Analytics. Enterprises analyzing high volumes of raw machine data can store them in a high performance NAS with a single namespace to facilitate analytics and processing. NAS enables far more analytics capabilities than other types of storage—metadata analytics, for example, like those offered through data virtualization, are being packaged with NAS solutions to let users better search and use their data.
- Visual imaging. NAS devices can support such high-end applications as rendering, microscopy, image processing, and 3-D animation, making them particularly useful for industries with those specific needs.
- Virtual Machines. NAS can be used to host virtual machines and improve speed and scalability, letting the virtualization process run faster.
- Smart homes. NAS also has applications in smart homes by creating a centralized media hub—with a single device, users can store data from CCTV, create a catalog of multimedia files, and stream on multiple devices at the same time.
Bottom Line: Why Choose NAS?
Network attached storage, or NAS, is cost-effective, affordable, and easy to scale. Because NAS functions like a private cloud, data is accessible and available to authorized users anytime, anyplace—as long as they have network access. Most cloud vendors also offer NAS solutions that let customers integrate both approaches to streamline efficiency and cost while maintaining better control over the security of their data.
NAS supports a wide range of applications, from basic file sharing and storage to media streaming to backup and recovery to collaboration, and can be used for everything from financial and accounting systems to business intelligence and data analytics. Scaled down, consumer-friendly versions are growing in popularity among home users and small businesses, while complex, high-performance NAS solutions are among the most widely used in enterprise environments across multiple industries.
Read next: 5 Types of Enterprise Data Storage



